How to Join FD-IX: A Simple, Step-by-Step Guide
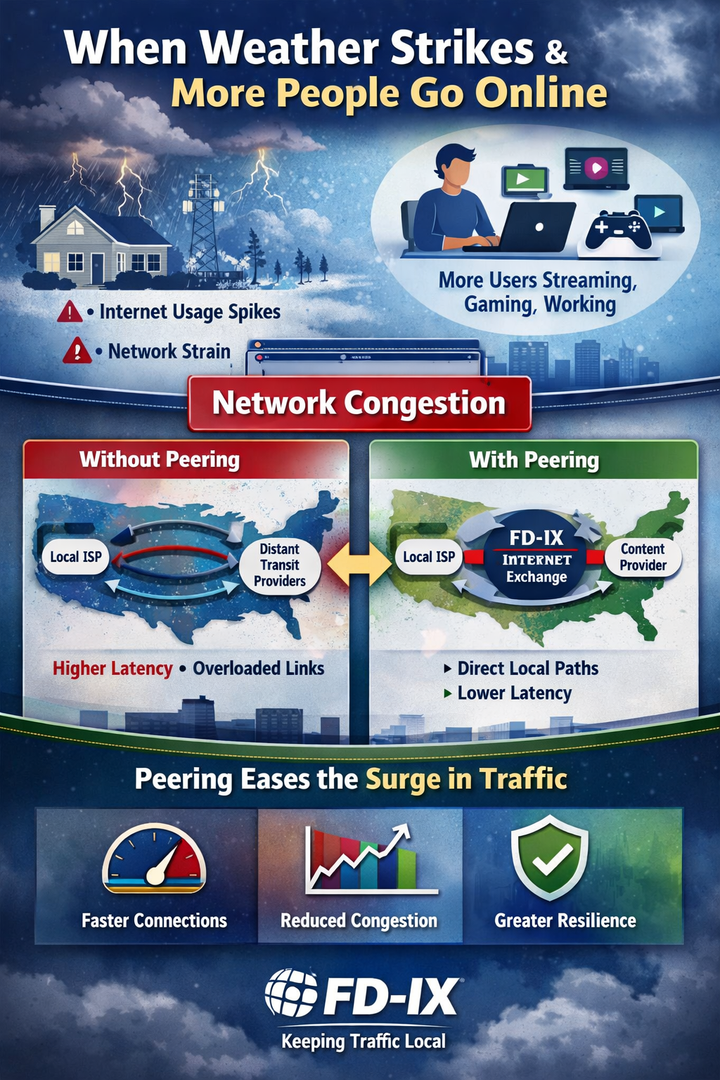
Joining FD-IX connects your network directly to other Internet providers, content networks, and cloud platforms. The result is faster paths, lower latency, and less reliance on paid transit.

Joining FD-IX connects your network directly to other Internet providers, content networks, and cloud platforms. The result is faster paths, lower latency, and less reliance on paid transit.
This guide walks through what to expect, from first contact to live traffic.
Step 1: Make Sure Your Network Is Ready
To join FD-IX, your network needs a few basics:
- A public Autonomous System Number (ASN)
- Your own IPv4 and or IPv6 address space
- A router capable of running Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
- A presence in, or access to, an FD-IX connected data center
Visit FD-IX.com and fill out our "get connected" form to get started.
Step 2: Review FD-IX Technical Guidelines
FD-IX publishes clear technical and acceptable use guidelines. These cover:
- How traffic is exchanged
- Routing and filtering expectations
- Route server availability
- Port speeds and media types
This step sets expectations early and helps avoid surprises later. Our support team can provide you with a document specific to your market.
Step 3: Order Your FD-IX Port
Choose the port size that fits your traffic needs. FD-IX offers multiple options, commonly including:
- 1G
- 10G
- 25G
- 100G
Many networks start at 10G for flexibility and room to grow.
Step 4: Install the Cross-Connect
A cross-connect links your router to the FD-IX switching fabric. This is usually a short fiber run inside the same data center.
At this stage, you will confirm:
- Fiber type
- Port speed
- Optics
- Hand-off details
FD-IX will issue what is called a Letter Of Authority (LOA) so you can order a cross-connect to us. Once complete, your network is physically connected to FD-IX.
Step 5: Configure Your Router Interface
FD-IX provides IPv4 and or IPv6 addresses for the exchange LAN.
On your router, you will:
- Create a dedicated interface for FD-IX
- Assign the provided IP addresses (IPv4 and IPv6
- Set the recommended MTU
- Enable basic monitoring and logging
- Disable spanning-tree,cdp,ldp and other protocols on the interface.
This interface is used only for peering traffic.
Step 6: Set Routing Policy First
Before any BGP sessions come up, routing policy should already be in place.
Good policy includes:
- Advertising only your own prefixes
- Filtering invalid or private routes inbound
- Setting prefix limits for safety
- Supporting RPKI
- Setting BGP attributes like Local-pref
This protects both your network and the exchange.
Step 7: Establish Peering Sessions
FD-IX supports two common peering models:
Route servers
You connect once and exchange routes with many members. This is the fastest way to start seeing value.
Direct bilateral peering
You form one-to-one sessions with specific networks, often for high-volume traffic.
Most members use both.
Step 8: Update Your PeeringDB Record
PeeringDB is how other networks learn about you.
A complete entry should include:
- ASN and network name
- Advertised prefixes
- NOC contact details
- Peering policy
- Ip addresses on the FD-IX peering fabric
An accurate record increases peering opportunities.
Step 9: Bring Sessions Online
Once BGP sessions are enabled, you will:
- Confirm sessions establish cleanly
- Verify prefix counts
- Ensure only intended routes are exchanged
Traffic usually begins shifting within minutes.
Step 10: Validate Performance
After traffic starts flowing, check:
- Latency improvements
- Reduced transit usage
- Traffic paths to common destinations
This is where the benefits of local peering become visible.
Step 11: Ongoing Operation and Growth
FD-IX is not a “plug it in and forget it” service.
Successful members:
- Monitor peering sessions
- Watch for routing changes
- Add new peers over time
- Keep routing data current
As your traffic grows, FD-IX grows with you.
Why Networks Choose FD-IX
FD-IX focuses on practical, engineer-friendly interconnection:
- Neutral, non-profit exchange model
- Multiple markets and expansion sites
- Route servers for fast onboarding
- A community built around cooperation, not lock-in
Peering at FD-IX lets your network keep traffic local and predictable.
Ready to Join?
If your network is ready to peer, the FD-IX team can guide you through the process and answer technical questions before any hardware is ordered.
Peering works best when it is simple, transparent, and well-run. That is the design goal behind FD-IX.